It is defined as the average mass of atoms of an element, which is calculated with the help of relative abundance of isotopes of a naturally occurring element. For example, the atomic mass of hydrogen is 1.0079 and carbon is 12.011. Atomic number is defined as the number of protons in an element. Average atomic mass = f 1 M 1 + f 2 M 2 + + f n M n where f is the fraction representing the natural abundance of the isotope and M is the mass number (weight) of the isotope. The average atomic mass of an element can be found on the periodic table, typically under the elemental symbol.
IUPAC Commission on Isotopic Abundances and Atomic Weights.- List of elements by atomic mass This is a list of chemical elements, sorted by atomic mass (or most stable isotope) and color coded according to type of element. Each element's atomic number, name, element symbol, and group and period numbers on the periodic table are given.
- Atomic Mass of Chemical Elements The atomic mass is the mass of an atom.
- Note that isotopic atomic species of a given element is uniquely identified by the mass number A, also called atomic mass number, which is the number of nucleons (protons and neutrons) in an atomic nucleus.
These tables are based on the 2015 table with changes from the 2015 table for the values of aluminium, argon, cobalt, gold, holmium, iridium, manganese, niobium, praseodymium, protactinium, rhodium, terbium, thulium and yttrium. See report 5 June 2018. The revised value of hafnium was reported 11 December 2019
Atomic Mass Of Elements List
https://www.qmul.ac.uk/sbcs/iupac/AtWt/
World Wide Web version of atomic weight data originally prepared by G. P. Moss, from a file provided by D. R. Lide.
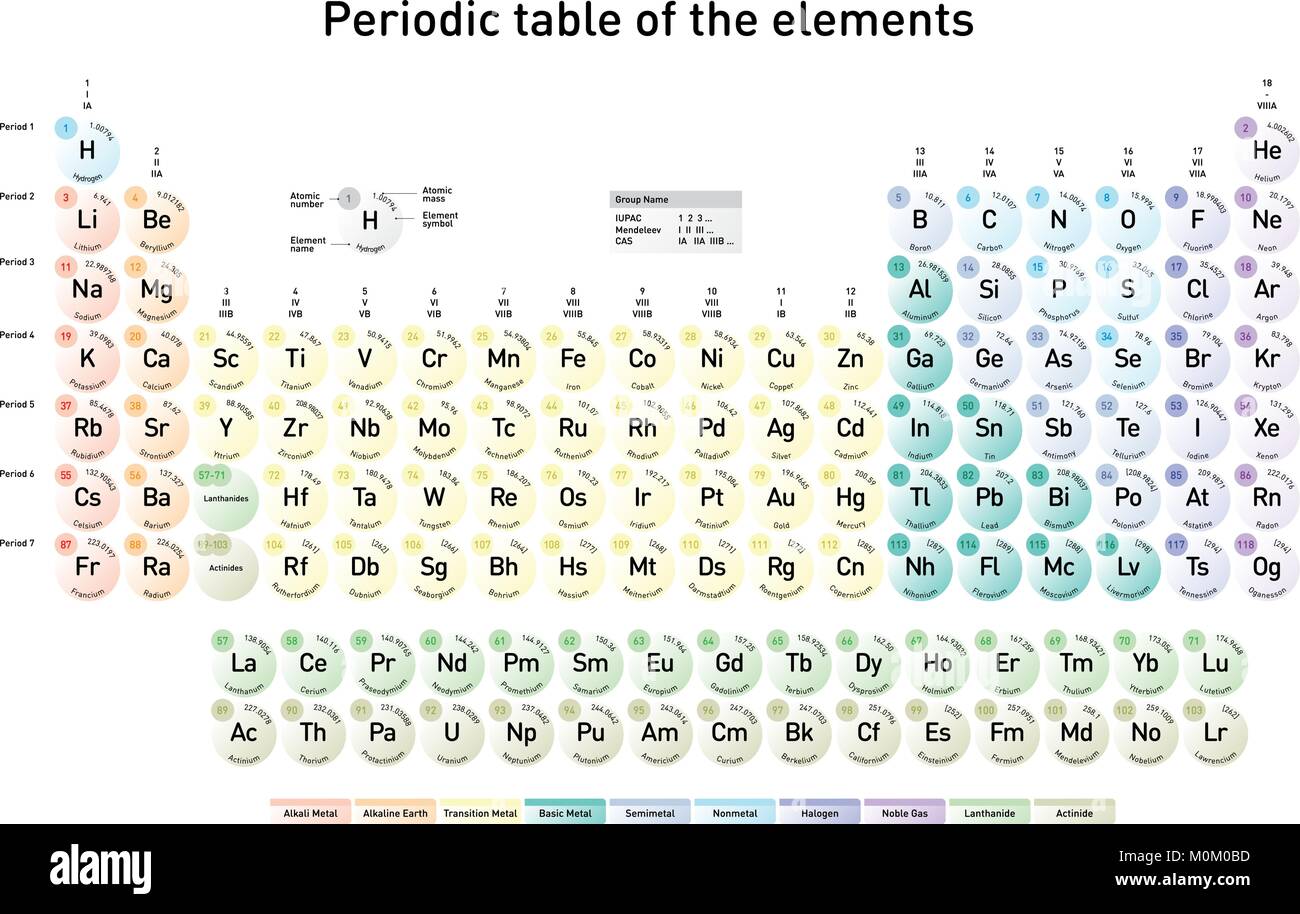
Previous values may be consulted from the 1993 table, the 1995 table, the 1997 table, the 1999 table, the 2001 table, the 2005 table, the 2007 table, the 2009 table, the 2011 table, the 2013 table or the 2015 table.
The standard atomic weights of twelve elements having two or more stable isotopes have variability of atomic-weight values in natural terrestrial materials. These are given in table 1 below. In the other lists the values quoted are those suggested for material where the origin of the sample is unknown. For radioactive elements the isotope with the longest half-life is quoted in parenthesis. The original paper should be consulted for full details of the variation in atomic weight and the half life of the radioisotopes quoted below.
Atomic Mass Of Elements Rounded Off
A number in parentheses indicates the uncertainty in the last digit of the atomic weight.
See below for the elements listed in Atomic Number Order or Name order.
See also a copy of the periodic table with atomic weights to five significant figures.
Table 1. List of Elements with Range of Atomic Weights.
| At No | Symbol | Name | Minimum Atomic Wt | Maximum Atomic Wt |
| 1 | H | hydrogen | 1.007 84 | 1.008 11 |
| 3 | Li | lithium | 6.938 | 6.997 |
| 5 | B | boron | 10.806 | 10.821 |
| 6 | C | carbon | 12.0096 | 12.0116 |
| 7 | N | nitrogen | 14.006 43 | 14.007 28 |
| 8 | O | oxygen | 15.999 03 | 15.999 77 |
| 12 | Mg | magnesium | 24.304 | 24.307 |
| 14 | Si | silicon | 28.084 | 28.086 |
| 16 | S | sulfur | 32.059 | 32.076 |
| 17 | Cl | chlorine | 35.446 | 35.457 |
| 18 | Ar | argon | 39.792 | 39.963 |
| 35 | Br | bromine | 79.901 | 79.907 |
| 81 | Tl | thallium | 204.382 | 204.385 |

See original paper for the range of these elements from different sources [Isotope-abundance variations and atomic weights of selected elements: 2016 (IUPAC Technical Report), Pure Appl. Chem. 2016, 88(12), 1203-1224.]
Table 2. List of Elements in Atomic Number Order.
| At No | Symbol | Name | Atomic Wt | Notes |
| 1 | H | Hydrogen | 1.008 | 3, 5 |
| 2 | He | Helium | 4.002 602(2) | 1, 2 |
| 3 | Li | Lithium | 6.94 | 3, 5 |
| 4 | Be | Beryllium | 9.012 1831(5) | |
| 5 | B | Boron | 10.81 | 3, 5 |
| 6 | C | Carbon | 12.011 | 5 |
| 7 | N | Nitrogen | 14.007 | 5 |
| 8 | O | Oxygen | 15.999 | 5 |
| 9 | F | Fluorine | 18.998 403 163(6) | |
| 10 | Ne | Neon | 20.1797(6) | 1, 3 |
| 11 | Na | Sodium | 22.989 769 28(2) | |
| 12 | Mg | Magnesium | 24.305 | 5 |
| 13 | Al | Aluminium | 26.981 5384(3) | |
| 14 | Si | Silicon | 28.085 | 5 |
| 15 | P | Phosphorus | 30.973 761 998(5) | |
| 16 | S | Sulfur | 32.06 | 5 |
| 17 | Cl | Chlorine | 35.45 | 3, 5 |
| 18 | Ar | Argon | 39.948(1) | 1, 2, 5 |
| 19 | K | Potassium | 39.0983(1) | |
| 20 | Ca | Calcium | 40.078(4) | |
| 21 | Sc | Scandium | 44.955 908(5) | |
| 22 | Ti | Titanium | 47.867(1) | |
| 23 | V | Vanadium | 50.9415(1) | |
| 24 | Cr | Chromium | 51.9961(6) | |
| 25 | Mn | Manganese | 54.938 043(2) | |
| 26 | Fe | Iron | 55.845(2) | |
| 27 | Co | Cobalt | 58.933 194(3) | |
| 28 | Ni | Nickel | 58.6934(4) | 2 |
| 29 | Cu | Copper | 63.546(3) | 2 |
| 30 | Zn | Zinc | 65.38(2) | 2 |
| 31 | Ga | Gallium | 69.723(1) | |
| 32 | Ge | Germanium | 72.630(8) | |
| 33 | As | Arsenic | 74.921 595(6) | |
| 34 | Se | Selenium | 78.971(8) | |
| 35 | Br | Bromine | 79.904 | 5 |
| 36 | Kr | Krypton | 83.798(2) | 1, 3 |
| 37 | Rb | Rubidium | 85.4678(3) | 1 |
| 38 | Sr | Strontium | 87.62(1) | 1, 2 |
| 39 | Y | Yttrium | 88.905 84(1) | |
| 40 | Zr | Zirconium | 91.224(2) | 1 |
| 41 | Nb | Niobium | 92.906 37(1) | |
| 42 | Mo | Molybdenum | 95.95(1) | 1 |
| 43 | Tc | Technetium | [97] | 4 |
| 44 | Ru | Ruthenium | 101.07(2) | 1 |
| 45 | Rh | Rhodium | 102.905 49(2) | |
| 46 | Pd | Palladium | 106.42(1) | 1 |
| 47 | Ag | Silver | 107.8682(2) | 1 |
| 48 | Cd | Cadmium | 112.414(4) | 1 |
| 49 | In | Indium | 114.818(1) | |
| 50 | Sn | Tin | 118.710(7) | 1 |
| 51 | Sb | Antimony | 121.760(1) | 1 |
| 52 | Te | Tellurium | 127.60(3) | 1 |
| 53 | I | Iodine | 126.904 47(3) | |
| 54 | Xe | Xenon | 131.293(6) | 1, 3 |
| 55 | Cs | Caesium | 132.905 451 96(6) | |
| 56 | Ba | Barium | 137.327(7) | |
| 57 | La | Lanthanum | 138.905 47(7) | 1 |
| 58 | Ce | Cerium | 140.116(1) | 1 |
| 59 | Pr | Praseodymium | 140.907 66(1) | |
| 60 | Nd | Neodymium | 144.242(3) | 1 |
| 61 | Pm | Promethium | [145] | |
| 62 | Sm | Samarium | 150.36(2) | 1 |
| 63 | Eu | Europium | 151.964(1) | 1 |
| 64 | Gd | Gadolinium | 157.25(3) | 1 |
| 65 | Tb | Terbium | 158.925 354(8) | |
| 66 | Dy | Dysprosium | 162.500(1) | 1 |
| 67 | Ho | Holmium | 164.930 328(7) | |
| 68 | Er | Erbium | 167.259(3) | 1 |
| 69 | Tm | Thulium | 168.934 218(6) | |
| 70 | Yb | Ytterbium | 173.045(10) | 1 |
| 71 | Lu | Lutetium | 174.9668(1) | 1 |
| 72 | Hf | Hafnium | 178.486(6) | |
| 73 | Ta | Tantalum | 180.947 88(2) | |
| 74 | W | Tungsten | 183.84(1) | |
| 75 | Re | Rhenium | 186.207(1) | |
| 76 | Os | Osmium | 190.23(3) | 1 |
| 77 | Ir | Iridium | 192.217(2) | |
| 78 | Pt | Platinum | 195.084(9) | |
| 79 | Au | Gold | 196.966 570(4) | |
| 80 | Hg | Mercury | 200.592(3) | |
| 81 | Tl | Thallium | 204.38 | 5 |
| 82 | Pb | Lead | 207.2(1) | 1, 2 |
| 83 | Bi | Bismuth | 208.980 40(1) | |
| 84 | Po | Polonium | [209] | 4 |
| 85 | At | Astatine | [210] | 4 |
| 86 | Rn | Radon | [222] | 4 |
| 87 | Fr | Francium | [223] | 4 |
| 88 | Ra | Radium | [226] | 4 |
| 89 | Ac | Actinium | [227] | 4 |
| 90 | Th | Thorium | 232.0377(4) | 1, 4 |
| 91 | Pa | Protactinium | 231.035 88(1) | 4 |
| 92 | U | Uranium | 238.028 91(3) | 1, 3, 4 |
| 93 | Np | Neptunium | [237] | 4 |
| 94 | Pu | Plutonium | [244] | 4 |
| 95 | Am | Americium | [243] | 4 |
| 96 | Cm | Curium | [247] | 4 |
| 97 | Bk | Berkelium | [247] | 4 |
| 98 | Cf | Californium | [251] | 4 |
| 99 | Es | Einsteinium | [252] | 4 |
| 100 | Fm | Fermium | [257] | 4 |
| 101 | Md | Mendelevium | [258] | 4 |
| 102 | No | Nobelium | [259] | 4 |
| 103 | Lr | Lawrencium | [262] | 4 |
| 104 | Rf | Rutherfordium | [267] | 4 |
| 105 | Db | Dubnium | [270] | 4 |
| 106 | Sg | Seaborgium | [269] | 4 |
| 107 | Bh | Bohrium | [270] | 4 |
| 108 | Hs | Hassium | [270] | 4 |
| 109 | Mt | Meitnerium | [278] | 4 |
| 110 | Ds | Darmstadtium | [281] | 4 |
| 111 | Rg | Roentgenium | [281] | 4 |
| 112 | Cn | Copernicium | [285] | 4 |
| 113 | Nh | Nihonium | [286] | 4 |
| 114 | Fl | Flerovium | [289] | 4 |
| 115 | Mc | Moscovium | [289] | 4 |
| 116 | Lv | Livermorium | [293] | 4 |
| 117 | Ts | Tennessine | [293] | 4 |
| 118 | Og | Oganesson | [294] | 4 |
- Geological specimens are known in which the element has an isotopic composition outside the limits for normal material. The difference between the atomic weight of the element in such specimens and that given in the Table may exceed the stated uncertainty.
- Range in isotopic composition of normal terrestrial material prevents a more precise value being given; the tabulated value should be applicable to any normal material.
- Modified isotopic compositions may be found in commercially available material because it has been subject to an undisclosed or inadvertant isotopic fractionation. Substantial deviations in atomic weight of the element from that given in the Table can occur.
- Element has no stable nuclides. The value enclosed in brackets, e.g. [209], indicates the mass number of the longest-lived isotope of the element. However three such elements (Th, Pa, and U) do have a characteristic terrestrial isotopic composition, and for these an atomic weight is tabulated.
- See table 1 for details of range and original paper for the atomic weight of the element from different sources.
Table 3. List of Elements in Name Order.
| At No | Symbol | Name | Atomic Wt | Notes |
| 89 | Ac | Actinium | [227] | 4 |
| 13 | Al | Aluminium | 26.981 5384(3) | |
| 95 | Am | Americium | [243] | 4 |
| 51 | Sb | Antimony | 121.760(1) | 1 |
| 18 | Ar | Argon | 39.948(1) | 1, 2, 5 |
| 33 | As | Arsenic | 74.921 595(6) | |
| 85 | At | Astatine | [210] | 4 |
| 56 | Ba | Barium | 137.327(7) | |
| 97 | Bk | Berkelium | [247] | 4 |
| 4 | Be | Beryllium | 9.012 1831(5) | |
| 83 | Bi | Bismuth | 208.980 40(1) | |
| 107 | Bh | Bohrium | [270] | 4 |
| 5 | B | Boron | 10.81 | 3, 5 |
| 35 | Br | Bromine | 79.904 | 5 |
| 48 | Cd | Cadmium | 112.414(4) | 1 |
| 55 | Cs | Caesium | 132.905 451 96(6) | |
| 20 | Ca | Calcium | 40.078(4) | 1 |
| 98 | Cf | Californium | [251] | 4 |
| 6 | C | Carbon | 12.011 | 5 |
| 58 | Ce | Cerium | 140.116(1) | 1 |
| 17 | Cl | Chlorine | 35.45 | 3, 5 |
| 24 | Cr | Chromium | 51.9961(6) | |
| 27 | Co | Cobalt | 58.933 194(3) | |
| 112 | Cn | Copernicium | [285] | 4 |
| 29 | Cu | Copper | 63.546(3) | 2 |
| 96 | Cm | Curium | [247] | 4 |
| 110 | Ds | Darmstadtium | [281] | 4 |
| 105 | Db | Dubnium | [270] | 4 |
| 66 | Dy | Dysprosium | 162.500(1) | 1 |
| 99 | Es | Einsteinium | [252] | 4 |
| 68 | Er | Erbium | 167.259(3) | 1 |
| 63 | Eu | Europium | 151.964(1) | 1 |
| 100 | Fm | Fermium | [257] | 4 |
| 114 | Fl | Flerovium | [289] | 4 |
| 9 | F | Fluorine | 18.998 403 163(6) | |
| 87 | Fr | Francium | [223] | 4 |
| 64 | Gd | Gadolinium | 157.25(3) | 1 |
| 31 | Ga | Gallium | 69.723(1) | |
| 32 | Ge | Germanium | 72.630(8) | |
| 79 | Au | Gold | 196.966 570(4) | |
| 72 | Hf | Hafnium | 178.486(6) | |
| 108 | Hs | Hassium | [270] | 4 |
| 2 | He | Helium | 4.002 602(2) | 1, 2 |
| 67 | Ho | Holmium | 164.930 328(7) | |
| 1 | H | Hydrogen | 1.008 | 3, 5 |
| 49 | In | Indium | 114.818(1) | |
| 53 | I | Iodine | 126.904 47(3) | |
| 77 | Ir | Iridium | 192.217(2) | |
| 26 | Fe | Iron | 55.845(2) | |
| 36 | Kr | Krypton | 83.798(2) | 1, 3 |
| 57 | La | Lanthanum | 138.905 47(7) | 1 |
| 103 | Lr | Lawrencium | [262] | 4 |
| 82 | Pb | Lead | 207.2(1) | 1, 2 |
| 3 | Li | Lithium | 6.94 | 3, 5 |
| 116 | Lv | Livermorium | [293] | 4 |
| 71 | Lu | Lutetium | 174.9668(1) | 1 |
| 12 | Mg | Magnesium | 24.305 | 5 |
| 25 | Mn | Manganese | 54.938 043(2) | |
| 109 | Mt | Meitnerium | [278] | 4 |
| 101 | Md | Mendelevium | [258] | 4 |
| 80 | Hg | Mercury | 200.592(3) | |
| 42 | Mo | Molybdenum | 95.95(1) | 1 |
| 115 | Mc | Moscovium | [289] | 4 |
| 60 | Nd | Neodymium | 144.242(3) | 1 |
| 10 | Ne | Neon | 20.1797(6) | 1, 3 |
| 93 | Np | Neptunium | [237] | 4 |
| 28 | Ni | Nickel | 58.6934(4) | |
| 113 | Nh | Nihonium | [286] | 4 |
| 41 | Nb | Niobium | 92.906 37(1) | |
| 7 | N | Nitrogen | 14.007 | 5 |
| 102 | No | Nobelium | [259] | 4 |
| 118 | Og | Oganesson | [294] | 4 |
| 76 | Os | Osmium | 190.23(3) | 1 |
| 8 | O | Oxygen | 15.999 | 5 |
| 46 | Pd | Palladium | 106.42(1) | 1 |
| 15 | P | Phosphorus | 30.973 761 998(5) | |
| 78 | Pt | Platinum | 195.084(9) | |
| 94 | Pu | Plutonium | [244] | 4 |
| 84 | Po | Polonium | [209] | 4 |
| 19 | K | Potassium | 39.0983(1) | |
| 59 | Pr | Praseodymium | 140.907 66(1) | |
| 61 | Pm | Promethium | [145] | 4 |
| 91 | Pa | Protactinium | 231.035 88(1) | 4 |
| 88 | Ra | Radium | [226] | 4 |
| 86 | Rn | Radon | [222] | 4 |
| 75 | Re | Rhenium | 186.207(1) | |
| 45 | Rh | Rhodium | 102.905 49(2) | |
| 111 | Rg | Roentgenium | [281] | 4 |
| 37 | Rb | Rubidium | 85.4678(3) | 1 |
| 44 | Ru | Ruthenium | 101.07(2) | 1 |
| 104 | Rf | Rutherfordium | [267] | 4 |
| 62 | Sm | Samarium | 150.36(2) | 1 |
| 21 | Sc | Scandium | 44.955 908(5) | |
| 106 | Sg | Seaborgium | [269] | 4 |
| 34 | Se | Selenium | 78.971(8) | |
| 14 | Si | Silicon | 28.085 | 5 |
| 47 | Ag | Silver | 107.8682(2) | 1 |
| 11 | Na | Sodium | 22.989 769 28(2) | |
| 38 | Sr | Strontium | 87.62(1) | 1, 2 |
| 16 | S | Sulfur | 32.06 | 5 |
| 73 | Ta | Tantalum | 180.947 88(2) | |
| 43 | Tc | Technetium | [97] | 4 |
| 52 | Te | Tellurium | 127.60(3) | 1 |
| 117 | Ts | Tennessine | [293] | 4 |
| 65 | Tb | Terbium | 158.925 354(8) | |
| 81 | Tl | Thallium | 204.38 | 5 |
| 90 | Th | Thorium | 232.0377(4) | 1, 4 |
| 69 | Tm | Thulium | 168.934 218(6) | |
| 50 | Sn | Tin | 118.710(7) | 1 |
| 22 | Ti | Titanium | 47.867(1) | |
| 74 | W | Tungsten | 183.84(1) | |
| 92 | U | Uranium | 238.028 91(3) | 1, 3, 4 |
| 23 | V | Vanadium | 50.9415(1) | |
| 54 | Xe | Xenon | 131.293(6) | 1, 3 |
| 70 | Yb | Ytterbium | 173.045(10) | 1 |
| 39 | Y | Yttrium | 88.905 84(1) | |
| 30 | Zn | Zinc | 65.38(2) | 2 |
| 40 | Zr | Zirconium | 91.224(2) | 1 |
- Geological specimens are known in which the element has an isotopic composition outside the limits for normal material. The difference between the atomic weight of the element in such specimens and that given in the Table may exceed the stated uncertainty.
- Range in isotopic composition of normal terrestrial material prevents a more precise value being given; the tabulated value should be applicable to any normal material.
- Modified isotopic compositions may be found in commercially available material because it has been subject to an undisclosed or inadvertant isotopic fractionation. Substantial deviations in atomic weight of the element from that given in the Table can occur.
- Element has no stable nuclides. The value enclosed in brackets, e.g. [209], indicates the mass number of the longest-lived isotope of the element. However three such elements (Th, Pa, and U) do have a characteristic terrestrial isotopic composition, and for these an atomic weight is tabulated.
- See table 1 for details of range and original paper for the atomic weight of the element from different sources.
Click a column header, such as Name, to sort the table by that item.
SEENotes at the bottom of the Table.
| No. | Atomic weight | Name | Sym. | M.P. (°C) | B.P. (°C) | Density* (g/cm3) | Earth crust (%)* | Discovery (Year) | Group* | Electron configuration | Ionization energy (eV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.008 | Hydrogen | H | -259 | -253 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 1776 | 1 | 1s1 | 13.60 | |
| 2 | 4.003 | Helium | He | -272 | -269 | 0.18 | 1895 | 18 | 1s2 | 24.59 | ||
| 3 | 6.941 | Lithium | Li | 180 | 1,347 | 0.53 | 1817 | 1 | [He] 2s1 | 5.39 | ||
| 4 | 9.012 | Beryllium | Be | 1,278 | 2,970 | 1.85 | 1797 | 2 | [He] 2s2 | 9.32 | ||
| 5 | 10.811 | Boron | B | 2,300 | 2,550 | 2.34 | 1808 | 13 | [He] 2s2 2p1 | 8.30 | ||
| 6 | 12.011 | Carbon | C | 3,500 | 4,827 | 2.26 | 0.09 | ancient | 14 | [He] 2s2 2p2 | 11.26 | |
| 7 | 14.007 | Nitrogen | N | -210 | -196 | 1.25 | 1772 | 15 | [He] 2s2 2p3 | 14.53 | ||
| 8 | 15.999 | Oxygen | O | -218 | -183 | 1.43 | 46.71 | 1774 | 16 | [He] 2s2 2p4 | 13.62 | |
| 9 | 18.998 | Fluorine | F | -220 | -188 | 1.70 | 0.03 | 1886 | 17 | [He] 2s2 2p5 | 17.42 | |
| 10 | 20.180 | Neon | Ne | -249 | -246 | 0.90 | 1898 | 18 | [He] 2s2 2p6 | 21.56 | ||
| 11 | 22.990 | Sodium | Na | 98 | 883 | 0.97 | 2.75 | 1807 | 1 | [Ne] 3s1 | 5.14 | |
| 12 | 24.305 | Magnesium | Mg | 639 | 1,090 | 1.74 | 2.08 | 1755 | 2 | [Ne] 3s2 | 7.65 | |
| 13 | 26.982 | Aluminum | Al | 660 | 2,467 | 2.70 | 8.07 | 1825 | 13 | [Ne] 3s2 3p1 | 5.99 | |
| 14 | 28.086 | Silicon | Si | 1,410 | 2,355 | 2.33 | 27.69 | 1824 | 14 | [Ne] 3s2 3p2 | 8.15 | |
| 15 | 30.974 | Phosphorus | P | 44 | 280 | 1.82 | 0.13 | 1669 | 15 | [Ne] 3s2 3p3 | 10.49 | |
| 16 | 32.065 | Sulfur | S | 113 | 445 | 2.07 | 0.05 | ancient | 16 | [Ne] 3s2 3p4 | 10.36 | |
| 17 | 35.453 | Chlorine | Cl | -101 | -35 | 3.21 | 0.05 | 1774 | 17 | [Ne] 3s2 3p5 | 12.97 | |
| 18 | 39.948 | Argon | Ar | -189 | -186 | 1.78 | 1894 | 18 | [Ne] 3s2 3p6 | 15.76 | ||
| 19 | 39.098 | Potassium | K | 64 | 774 | 0.86 | 2.58 | 1807 | 1 | [Ar] 4s1 | 4.34 | |
| 20 | 40.078 | Calcium | Ca | 839 | 1,484 | 1.55 | 3.65 | 1808 | 2 | [Ar] 4s2 | 6.11 | |
| 21 | 44.956 | Scandium | Sc | 1,539 | 2,832 | 2.99 | 1879 | 3 | [Ar] 3d1 4s2 | 6.56 | ||
| 22 | 47.867 | Titanium | Ti | 1,660 | 3,287 | 4.54 | 0.62 | 1791 | 4 | [Ar] 3d2 4s2 | 6.83 | |
| 23 | 50.942 | Vanadium | V | 1,890 | 3,380 | 6.11 | 1830 | 5 | [Ar] 3d3 4s2 | 6.75 | ||
| 24 | 51.996 | Chromium | Cr | 1,857 | 2,672 | 7.19 | 0.04 | 1797 | 6 | [Ar] 3d5 4s1 | 6.77 | |
| 25 | 54.938 | Manganese | Mn | 1,245 | 1,962 | 7.43 | 0.09 | 1774 | 7 | [Ar] 3d5 4s2 | 7.43 | |
| 26 | 55.845 | Iron | Fe | 1,535 | 2,750 | 7.87 | 5.05 | ancient | 8 | [Ar] 3d6 4s2 | 7.90 | |
| 27 | 58.933 | Cobalt | Co | 1,495 | 2,870 | 8.90 | 1735 | 9 | [Ar] 3d7 4s2 | 7.88 | ||
| 28 | 58.693 | Nickel | Ni | 1,453 | 2,732 | 8.90 | 0.02 | 1751 | 10 | [Ar] 3d8 4s2 | 7.64 | |
| 29 | 63.546 | Copper | Cu | 1,083 | 2,567 | 8.96 | ancient | 11 | [Ar] 3d10 4s1 | 7.73 | ||
| 30 | 65.390 | Zinc | Zn | 420 | 907 | 7.13 | ancient | 12 | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 | 9.39 | ||
| 31 | 69.723 | Gallium | Ga | 30 | 2,403 | 5.91 | 1875 | 13 | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p1 | 6.00 | ||
| 32 | 72.640 | Germanium | Ge | 937 | 2,830 | 5.32 | 1886 | 14 | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p2 | 7.90 | ||
| 33 | 74.922 | Arsenic | As | 81 | 613 | 5.72 | ancient | 15 | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3 | 9.79 | ||
| 34 | 78.960 | Selenium | Se | 217 | 685 | 4.79 | 1817 | 16 | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p4 | 9.75 | ||
| 35 | 79.904 | Bromine | Br | -7 | 59 | 3.12 | 1826 | 17 | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p5 | 11.81 | ||
| 36 | 83.800 | Krypton | Kr | -157 | -153 | 3.75 | 1898 | 18 | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p6 | 14.00 | ||
| 37 | 85.468 | Rubidium | Rb | 39 | 688 | 1.63 | 1861 | 1 | [Kr] 5s1 | 4.18 | ||
| 38 | 87.620 | Strontium | Sr | 769 | 1,384 | 2.54 | 1790 | 2 | [Kr] 5s2 | 5.69 | ||
| 39 | 88.906 | Yttrium | Y | 1,523 | 3,337 | 4.47 | 1794 | 3 | [Kr] 4d1 5s2 | 6.22 | ||
| 40 | 91.224 | Zirconium | Zr | 1,852 | 4,377 | 6.51 | 0.03 | 1789 | 4 | [Kr] 4d2 5s2 | 6.63 | |
| 41 | 92.906 | Niobium | Nb | 2,468 | 4,927 | 8.57 | 1801 | 5 | [Kr] 4d4 5s1 | 6.76 | ||
| 42 | 95.940 | Molybdenum | Mo | 2,617 | 4,612 | 10.22 | 1781 | 6 | [Kr] 4d5 5s1 | 7.09 | ||
| 43 | * | 98.000 | Technetium | Tc | 2,200 | 4,877 | 11.50 | 1937 | 7 | [Kr] 4d5 5s2 | 7.28 | |
| 44 | 101.070 | Ruthenium | Ru | 2,250 | 3,900 | 12.37 | 1844 | 8 | [Kr] 4d7 5s1 | 7.36 | ||
| 45 | 102.906 | Rhodium | Rh | 1,966 | 3,727 | 12.41 | 1803 | 9 | [Kr] 4d8 5s1 | 7.46 | ||
| 46 | 106.420 | Palladium | Pd | 1,552 | 2,927 | 12.02 | 1803 | 10 | [Kr] 4d10 | 8.34 | ||
| 47 | 107.868 | Silver | Ag | 962 | 2,212 | 10.50 | ancient | 11 | [Kr] 4d10 5s1 | 7.58 | ||
| 48 | 112.411 | Cadmium | Cd | 321 | 765 | 8.65 | 1817 | 12 | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 | 8.99 | ||
| 49 | 114.818 | Indium | In | 157 | 2,000 | 7.31 | 1863 | 13 | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p1 | 5.79 | ||
| 50 | 118.710 | Tin | Sn | 232 | 2,270 | 7.31 | ancient | 14 | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p2 | 7.34 | ||
| 51 | 121.760 | Antimony | Sb | 630 | 1,750 | 6.68 | ancient | 15 | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p3 | 8.61 | ||
| 52 | 127.600 | Tellurium | Te | 449 | 990 | 6.24 | 1783 | 16 | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p4 | 9.01 | ||
| 53 | 126.905 | Iodine | I | 114 | 184 | 4.93 | 1811 | 17 | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p5 | 10.45 | ||
| 54 | 131.293 | Xenon | Xe | -112 | -108 | 5.90 | 1898 | 18 | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p6 | 12.13 | ||
| 55 | 132.906 | Cesium | Cs | 29 | 678 | 1.87 | 1860 | 1 | [Xe] 6s1 | 3.89 | ||
| 56 | 137.327 | Barium | Ba | 725 | 1,140 | 3.59 | 0.05 | 1808 | 2 | [Xe] 6s2 | 5.21 | |
| 57 | 138.906 | Lanthanum | La | 920 | 3,469 | 6.15 | 1839 | 3 | [Xe] 5d1 6s2 | 5.58 | ||
| 58 | 140.116 | Cerium | Ce | 795 | 3,257 | 6.77 | 1803 | 101 | [Xe] 4f1 5d1 6s2 | 5.54 | ||
| 59 | 140.908 | Praseodymium | Pr | 935 | 3,127 | 6.77 | 1885 | 101 | [Xe] 4f3 6s2 | 5.47 | ||
| 60 | 144.240 | Neodymium | Nd | 1,010 | 3,127 | 7.01 | 1885 | 101 | [Xe] 4f4 6s2 | 5.53 | ||
| 61 | * | 145.000 | Promethium | Pm | 1,100 | 3,000 | 7.30 | 1945 | 101 | [Xe] 4f5 6s2 | 5.58 | |
| 62 | 150.360 | Samarium | Sm | 1,072 | 1,900 | 7.52 | 1879 | 101 | [Xe] 4f6 6s2 | 5.64 | ||
| 63 | 151.964 | Europium | Eu | 822 | 1,597 | 5.24 | 1901 | 101 | [Xe] 4f7 6s2 | 5.67 | ||
| 64 | 157.250 | Gadolinium | Gd | 1,311 | 3,233 | 7.90 | 1880 | 101 | [Xe] 4f7 5d1 6s2 | 6.15 | ||
| 65 | 158.925 | Terbium | Tb | 1,360 | 3,041 | 8.23 | 1843 | 101 | [Xe] 4f9 6s2 | 5.86 | ||
| 66 | 162.500 | Dysprosium | Dy | 1,412 | 2,562 | 8.55 | 1886 | 101 | [Xe] 4f10 6s2 | 5.94 | ||
| 67 | 164.930 | Holmium | Ho | 1,470 | 2,720 | 8.80 | 1867 | 101 | [Xe] 4f11 6s2 | 6.02 | ||
| 68 | 167.259 | Erbium | Er | 1,522 | 2,510 | 9.07 | 1842 | 101 | [Xe] 4f12 6s2 | 6.11 | ||
| 69 | 168.934 | Thulium | Tm | 1,545 | 1,727 | 9.32 | 1879 | 101 | [Xe] 4f13 6s2 | 6.18 | ||
| 70 | 173.040 | Ytterbium | Yb | 824 | 1,466 | 6.90 | 1878 | 101 | [Xe] 4f14 6s2 | 6.25 | ||
| 71 | 174.967 | Lutetium | Lu | 1,656 | 3,315 | 9.84 | 1907 | 101 | [Xe] 4f14 5d1 6s2 | 5.43 | ||
| 72 | 178.490 | Hafnium | Hf | 2,150 | 5,400 | 13.31 | 1923 | 4 | [Xe] 4f14 5d2 6s2 | 6.83 | ||
| 73 | 180.948 | Tantalum | Ta | 2,996 | 5,425 | 16.65 | 1802 | 5 | [Xe] 4f14 5d3 6s2 | 7.55 | ||
| 74 | 183.840 | Tungsten | W | 3,410 | 5,660 | 19.35 | 1783 | 6 | [Xe] 4f14 5d4 6s2 | 7.86 | ||
| 75 | 186.207 | Rhenium | Re | 3,180 | 5,627 | 21.04 | 1925 | 7 | [Xe] 4f14 5d5 6s2 | 7.83 | ||
| 76 | 190.230 | Osmium | Os | 3,045 | 5,027 | 22.60 | 1803 | 8 | [Xe] 4f14 5d6 6s2 | 8.44 | ||
| 77 | 192.217 | Iridium | Ir | 2,410 | 4,527 | 22.40 | 1803 | 9 | [Xe] 4f14 5d7 6s2 | 8.97 | ||
| 78 | 195.078 | Platinum | Pt | 1,772 | 3,827 | 21.45 | 1735 | 10 | [Xe] 4f14 5d9 6s1 | 8.96 | ||
| 79 | 196.967 | Gold | Au | 1,064 | 2,807 | 19.32 | ancient | 11 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s1 | 9.23 | ||
| 80 | 200.590 | Mercury | Hg | -39 | 357 | 13.55 | ancient | 12 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 | 10.44 | ||
| 81 | 204.383 | Thallium | Tl | 303 | 1,457 | 11.85 | 1861 | 13 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p1 | 6.11 | ||
| 82 | 207.200 | Lead | Pb | 327 | 1,740 | 11.35 | ancient | 14 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p2 | 7.42 | ||
| 83 | 208.980 | Bismuth | Bi | 271 | 1,560 | 9.75 | ancient | 15 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p3 | 7.29 | ||
| 84 | * | 209.000 | Polonium | Po | 254 | 962 | 9.30 | 1898 | 16 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p4 | 8.42 | |
| 85 | * | 210.000 | Astatine | At | 302 | 337 | 0.00 | 1940 | 17 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p5 | 9.30 | |
| 86 | * | 222.000 | Radon | Rn | -71 | -62 | 9.73 | 1900 | 18 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p6 | 10.75 | |
| 87 | * | 223.000 | Francium | Fr | 27 | 677 | 0.00 | 1939 | 1 | [Rn] 7s1 | 4.07 | |
| 88 | * | 226.000 | Radium | Ra | 700 | 1,737 | 5.50 | 1898 | 2 | [Rn] 7s2 | 5.28 | |
| 89 | * | 227.000 | Actinium | Ac | 1,050 | 3,200 | 10.07 | 1899 | 3 | [Rn] 6d1 7s2 | 5.17 | |
| 90 | 232.038 | Thorium | Th | 1,750 | 4,790 | 11.72 | 1829 | 102 | [Rn] 6d2 7s2 | 6.31 | ||
| 91 | 231.036 | Protactinium | Pa | 1,568 | 0 | 15.40 | 1913 | 102 | [Rn] 5f2 6d1 7s2 | 5.89 | ||
| 92 | 238.029 | Uranium | U | 1,132 | 3,818 | 18.95 | 1789 | 102 | [Rn] 5f3 6d1 7s2 | 6.19 | ||
| 93 | * | 237.000 | Neptunium | Np | 640 | 3,902 | 20.20 | 1940 | 102 | [Rn] 5f4 6d1 7s2 | 6.27 | |
| 94 | * | 244.000 | Plutonium | Pu | 640 | 3,235 | 19.84 | 1940 | 102 | [Rn] 5f6 7s2 | 6.03 | |
| 95 | * | 243.000 | Americium | Am | 994 | 2,607 | 13.67 | 1944 | 102 | [Rn] 5f7 7s2 | 5.97 | |
| 96 | * | 247.000 | Curium | Cm | 1,340 | 0 | 13.50 | 1944 | 102 | 5.99 | ||
| 97 | * | 247.000 | Berkelium | Bk | 986 | 0 | 14.78 | 1949 | 102 | 6.20 | ||
| 98 | * | 251.000 | Californium | Cf | 900 | 0 | 15.10 | 1950 | 102 | 6.28 | ||
| 99 | * | 252.000 | Einsteinium | Es | 860 | 0 | 0.00 | 1952 | 102 | 6.42 | ||
| 100 | * | 257.000 | Fermium | Fm | 1,527 | 0 | 0.00 | 1952 | 102 | 6.50 | ||
| 101 | * | 258.000 | Mendelevium | Md | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1955 | 102 | 6.58 | ||
| 102 | * | 259.000 | Nobelium | No | 827 | 0 | 0.00 | 1958 | 102 | 6.65 | ||
| 103 | * | 262.000 | Lawrencium | Lr | 1,627 | 0 | 0.00 | 1961 | 102 | 4.90 | ||
| 104 | * | 261.000 | Rutherfordium | Rf | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1964 | 4 | 0.00 | ||
| 105 | * | 262.000 | Dubnium | Db | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1967 | 5 | 0.00 | ||
| 106 | * | 266.000 | Seaborgium | Sg | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1974 | 6 | 0.00 | ||
| 107 | * | 264.000 | Bohrium | Bh | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1981 | 7 | 0.00 | ||
| 108 | * | 277.000 | Hassium | Hs | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1984 | 8 | 0.00 | ||
| 109 | * | 268.000 | Meitnerium | Mt | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1982 | 9 | 0.00 | ||
| No. | Atomic weight | Name | Sym. | M.P. (°C) | B.P. (°C) | Density* (g/cm3) | Earth crust (%)* | Discovery (Year) | Group* | Electron configuration | Ionization energy (eV) |
Notes:
• Density of elements with boiling points below 0°C is given in g/l. In a sorted list, these elements are shown before other elements that have boiling points >0°C.
• Earth crust composition average values are from a report by F. W. Clarke and H. S. Washington, 1924. Elemental composition of crustal rocks differ between different localities (see article).
• Group: There are only 18 groups in the periodic table that constitute the columns of the table. Lanthanoids and Actinoids are numbered as 101 and 102 to separate them in sorting by group.
• The elements marked with an asterisk (in the 2nd column) have no stable nuclides. For these elements the weight value shown represents the mass number of the longest-lived isotope of the element.
Abbreviations and Definitions:
No. - Atomic Number; M.P. - melting point; B.P. - boiling point
Atomic number: The number of protons in an atom. Each element is uniquely defined by its atomic number.
Atomic mass: The mass of an atom is primarily determined by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Atomic mass is measured in Atomic Mass Units (amu) which are scaled relative to carbon, 12C, that is taken as a standard element with an atomic mass of 12. This isotope of carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. Thus, each proton and neutron has a mass of about 1 amu.
Atomic Mass Table
Isotope: Atoms of the same element with the same atomic number, but different number of neutrons. Isotope of an element is defined by the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Elements have more than one isotope with varying numbers of neutrons. For example, there are two common isotopes of carbon, 12C and 13C which have 6 and 7 neutrons respectively. The abundances of different isotopes of elements vary in nature depending on the source of materials. For relative abundances of isotopes in nature see reference on Atomic Weights and Isotopic Compositions.
Atomic weight: Atomic weight values represent weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element. The values shown here are based on the IUPAC Commission determinations (Pure Appl. Chem. 73:667-683, 2001). The elements marked with an asterisk have no stable nuclides. For these elements the weight value shown represents the mass number of the longest-lived isotope of the element.
Electron configuration: See next page for explanation of electron configuration of atoms.
Ionization energy (IE): The energy required to remove the outermost electron from an atom or a positive ion in its ground level. The table lists only the first IE in eV units. To convert to kJ/mol multiply by 96.4869. Reference: NIST Reference Table on Ground states and ionization energies for the neutral atoms. IE decreases going down a column of the periodic table, and increases from left to right in a row. Thus, alkali metals have the lowest IE in a period and Rare gases have the highest.
Atomic Mass Of Elements Pdf

Atomic Mass Of Elements On The Periodic Table
Other resources related to the Periodic Table
Atomic Mass Of Elements Pdf
- Chemical Evolution of the Universe
